The potential of 5G connectivity is almost limitless, and the statistics are hard to imagine. Analysts predict that global 5G connections will double to 1.34 billion in 2022 and grow to 3.6 billion in 2025.
The global MARKET size of 5G services is $65.26 billion by 2021, with an estimated compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 25.9% and a value of $327.83 billion by 2028.
AT&T, T-Mobile and Verizon Wireless are racing to install their 5G infrastructure across the US and offer technology designed to achieve speeds of up to 20 Gbps with very low latency. Mobile data usage grew 200-fold between
2010 and 2020 and is expected to grow 20,000-fold.
But we're not in 5G yet.
For now, 5G's advantages are most evident in personal devices like smartphones and home appliances like smart thermostats. But as the rollout of 5G gains momentum, the impact will be huge. Data-intensive applications that benefit from real-time communication will make significant progress. These include self-driving cars, robotic surgery, medical wearables, traffic management and, of course, IIoT(Industrial Internet of Things) in today's smart factory

What does all this have to do with connectors?
Electrical connectors are a critical part of the infrastructure that supports 5G connections. They act as vital links between the cables that carry data and the devices that carry information, which have multiplied. Advances in high-speed data transmission have driven innovations in connector design in terms of performance, size, and electromagnetic signal interference (EMI) shielding. Different versions and sizes are used in communication applications, but the M16 connector has become the preferred 5G antenna.
For cellular tower antennas, the need for faster and more reliable data transmission has driven the development of connectors that can support specific requirements. Developed by antenna Interface Standard Group (AISG). AISG defines the communication interface for mobile phone antenna "Remote Electric Tilt" (RET). The AISG standard helps define AISG connectors for RS-485 (AISG C485) for outdoor applications. AISG standards have been redefined in terms of electrical and mechanical properties, environmental conditions and materials
As 5G networks and other high-speed data transmission applications grow in size each year, connectors have been getting smaller. The circular connector faces the challenge of saving space and weight and handling lightning-fast speeds, while continuing to provide reliability and robustness against the harsh conditions 5G cellular towers face. This requires design engineers to strike a balance between performance and reliability. The optimal balance will largely depend on the application and working with the customer to ensure that all criteria are met. However, today almost every market, not just the communications market, requires high performance and durability in smaller packages, so investment in design is critical to the success of vendors.
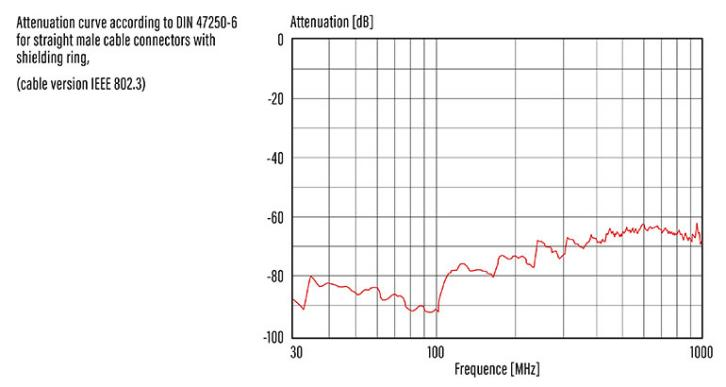
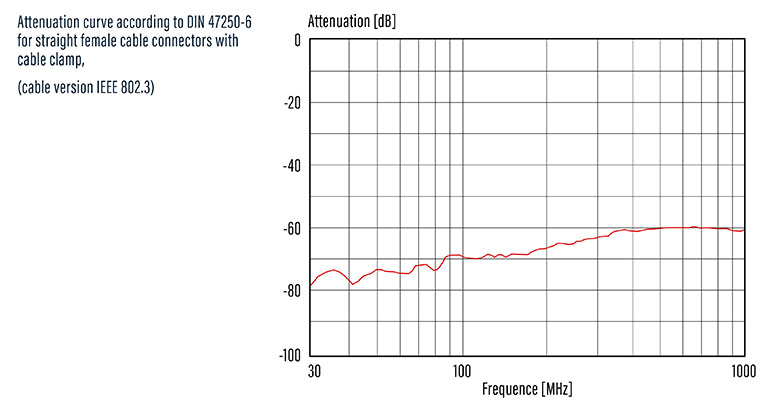
EMI shielding
Because buildings and other physical objects block 5G radio frequencies, millions of phones, computers and smart devices pose huge damage potential from EMI. The most effective defense against EMI is filtering at the connector interface. Optimized 360° EMC(electromagnetic compatibility) shielding of the M16 connector provides maximum integrity for sensitive signal and power connections. The shield is metal and can be used as a cable clip or shield ring.
The circular connector market is promising
The global connector market was worth $64.17 billion at the end of 2019. It is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 6.7% from 2020 to 2027, with a market size of more than $98 billion by 2027.
This number includes all connector types -- electrical, I/O, circular, printed circuit board (PCB), and others. Circular connectors account for about 7% of the overall market, with sales of $4.3 billion in 2020.
As 5G, IIoT and other industry 4.0 applications expand, the need for connectors with higher performance, smaller and lighter will also increase.
Post time: Jun-21-2022





